Supported by science.
In several in-vitro human skeletal muscle cell studies, Cellular Hydration™ was found to positively support muscle strength, endurance and recovery.
In collaboration with Denova Sciences, we conducted several in-vitro studies to determine our formula's effect on mitochondrial activity and muscle damage during and after exercise.
How we tested
Human skeletal muscle cell culture
SKMC were obtained from Lonza. Cells were maintained in SkGM™-2 media supplemented with growth factors in 5% CO2 incubator set at 37°C.
Cell proliferation
Cells were seeded onto 24 well plates. After 72 hours of treatment, cells were treated with 200 μl of 1 mg/mL of MTT for 2 hours at 37°C, in dark. After which media was removed, and 100 μl of DMSO was added to each well, followed by incubation for 1 hour at room temperature with shaking. Absorbance reading was taken at 570 nm wavelength, with the reference wavelength at 650 nm using Biotek Synergy HTX Automated Multi-Mode Reader.
RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR
To extract RNA from mammalian cells, RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) was used, according to the manufacturer’s protocol (genomic DNA was not removed using this kit). RNA was used as template for synthesis of cDNA using iScript™ reverse transcription supermix for RT-PCR (Bio Rad) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) samples were diluted and used as templates for real time PCR. Samples were run on Biorad CFX Connect Realtime PCR system using default settings for SYBR green reaction. Gene expression of mitochondria copy number POLG2 levels were calculated by ΔΔCT and normalized using GAPDH as endogenous control.

LDH
Cells were seeded in SKMC media and incubated with treatment for 48 hours at 37°C incubator with 5% CO2. Cells were washed twice with 500 μl of 1x phosphate-buffered saline and cells were lysed and prepared for the Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay Kit (colorimetric) (ab102526 Abcam) analysis, performed according to manufacturer’s protocol. LDH activity (mU/ml) was normalised with total protein concentration (μg/ml). Total protein concentration was determined using Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (23225, Thermo Scientific), performed according to manufacturer’s protocol. Relative LDH activity is calculated by dividing normalised LDH of treatment by control.
Creatine kinase
Cells were seeded in SKMC media and incubated with treatment for 48 hours at 37°C incubator with 5% CO2. Cells were washed twice with 500 μl of 1x phosphate-buffered saline and cells were lysed and prepared for the Creatine Kinase Assay Kit (colorimetric) (ab155901, Abcam) analysis, performed according to manufacturer’s protocol. Creatine Kinase activity (mU/ml) was normalised with total protein concentration (μg/ml). Total protein concentration was determined using Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (23225, Thermo Scientific), performed according to manufacturer’s protocol. Relative Creatine Kinase activity is calculated by dividing normalised LDH of treatment by control.
Mitochondrial staining
Cells were seeded on chambered-coverslip and incubated with treatment for 24 hr at 37°C incubator with 5% CO2. Cells were treated with 200 nM MitoTracker® Red CMXRos (#9082, Cell Signaling Technology) for 30 min. Cells were washed with 200 μl of 1x phosphate-buffered saline and fixed with 10% formalin for 30 min at room temperature. Samples were imaged on Zeiss LSM710 Confocal Microscope using Plan-Apochromat 63x/1.4 NA Oil Len. Images were processed and quantified using Image J software.
Results
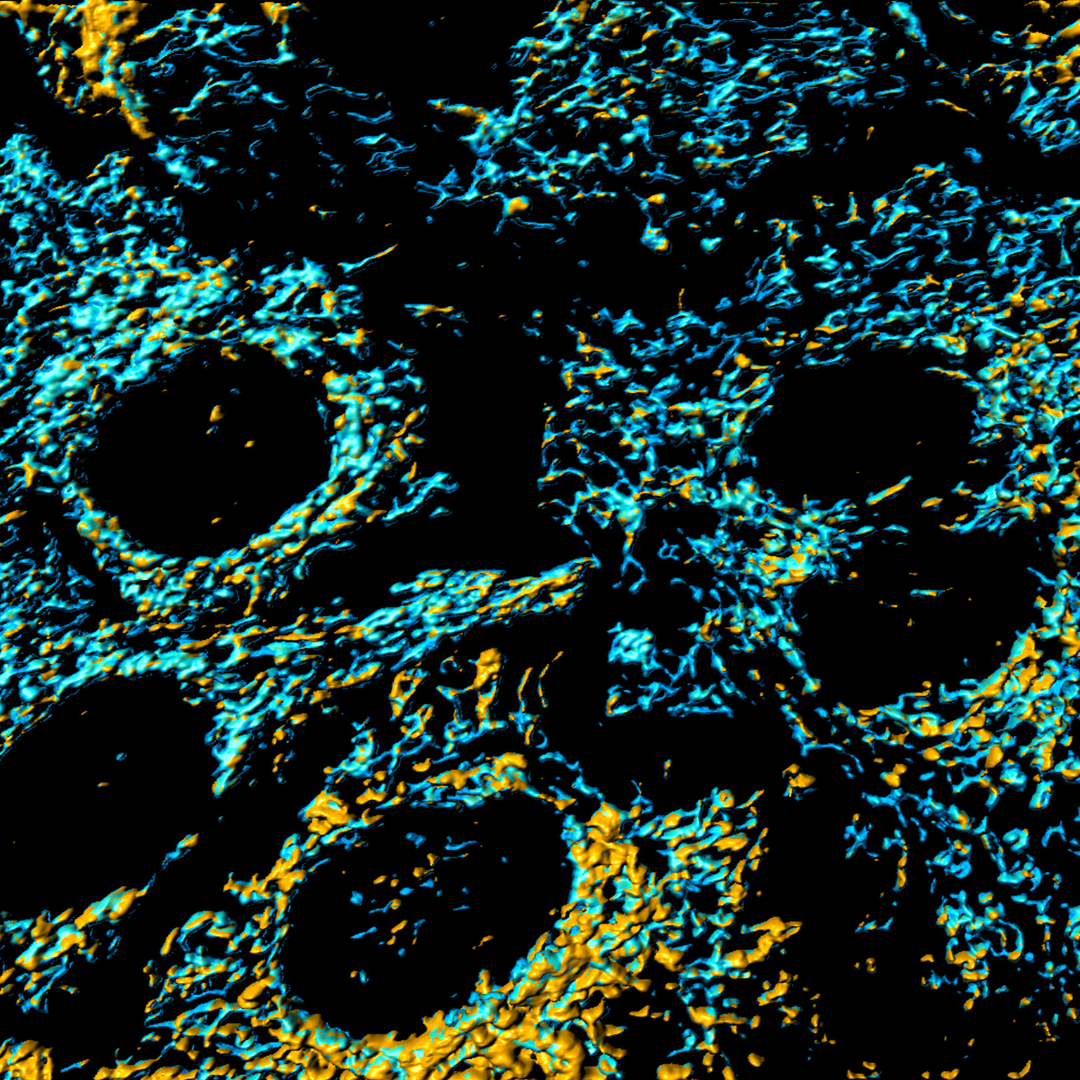
48% increase in mitochondrial energy production.
We evaluated whether adding Cellular Hydration™ to skeletal muscle cells can increase mitochondrial copy number.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, play a crucial role in generating the energy needed for cellular functions. Increasing the number of mitochondria can significantly boost energy production in muscle cells, leading to enhanced performance during workouts. This boost in mitochondrial density translates to greater, strength, and overall athletic performance.
Study result: Third Party Laboratory test showed that Cellular Hydration™ increased mitochondrial copy number by 48%. That’s great news for your body’s energy production during exercise.
Up to
27% increase in mitochondria activity in stress-induced skeletal muscle.
We evaluated whether adding Cellular Hydration™ to skeletal muscle cells can increase mitochondria activity under normal and stress-induced conditions.
Study result: Cellular Hydration™ had increased mitochondria intensity by 31% in normal muscle cells and 27% in stress-induced muscle cells (using an oxidation agent, H2O2). This might suggest a better protect-and-recover effect of Cellular Hydration™ during a workout.

Up to
92% reduction in muscle damage during exercise.
We evaluated whether adding Cellular Hydration™ to skeletal muscle cells can reduce muscle damage and fatigue onset, which hinder endurance during a workout.
Biomarkers creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are commonly used to measure tissue damage. Lower levels of CK and LDH mean less tissue damage, and vice-versa.
In this study, Cellular Hydration™ was added to skeletal muscle cells before they underwent oxidative stress (H2O2) to simulate the potential protective effects of consumption before a workout.
Study result: Cellular Hydration™ had reduced CK protein levels by 64% and LDH protein levels by 92%. If you’re looking to boost endurance during exercise, drinking Cellular Hydration™ can help you go the extra mile.

Up to
83% reduction in muscle damage after exercise.
We evaluated whether adding Cellular Hydration™ to “stress” skeletal muscle cells can reduce muscle damage and fatigue onset, which hinder recovery after a workout.
In this study, Cellular Hydration™ was added to skeletal muscle cells after they underwent oxidative stress (H2O2) to simulate effects of consumption after a workout.
Study result: Cellular Hydration™ had reduced CK protein levels by 80% and LDH protein levels by 83%. Anyone serious about performance would acknowledge that recovery after exercise is important, and Cellular Hydration™ can help you bounce back to optimal state.
